Take the survey to let me know what you like and dislike about PrincessStarfreckles! Be honest, I don't know who says what, only what is said. :)
Survey
Tuesday, May 29, 2012
Tuesday, April 3, 2012
Light Pollution
Did you know.....
60% of Americans live where the Milky Way is no longer even faintly visible?
50% of children worldwide will never see the Milky Way ever?
Of those 50%, 48% live in either the U.S, Canada, Europe or Asia?
1.5% live in the Middle East?
0.5% live in suburnized areas of Africa and South America?
The skyglow caused by London streetlights blocks stars and can be seen 125 miles away in French rural towns?
Worldwide, light pollution rises approximately 6% every year. It's estimated that by the end of the decade all Americans will live where the Milky Way is no longer visible, 90% of children will never see the Milky Way, and 50% of children will never see any stars, only the moon. Pretty scary statistics for amateur backyard astronomers.
 San Francisco skyglow
San Francisco skyglow
 Un-polluted night sky in a U.S. national park
Un-polluted night sky in a U.S. national park
April is Global Astronomy Month, so what better time to celebrate the night skies and educate about the effects of light pollution than now? The International Dark-Sky Associaton is fighting governments to pass laws to reduce the skyward-fixed lights and use lights that don't send off long-range light waves. The IDA has successfully caused over 300 cities to switch to better lighting that does not block out the night sky. Click here to learn more about the International Dark-Sky Association.
Globe at Night is another group dedicated to preserving our night skies. Every month, people world wide make observations of the night sky and send their results to Globe at Night. Globe at Night records the data and uses it to track the spread and growth of light pollution. The last opportunity to participate in Globe at Night for the next few months will be April 11-20. Click here to find out how.
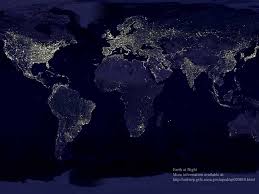 World light pollution
World light pollution
In addition to participating in Globe at Night, I am a member of the Dark Sky Society, which is seperate from the International Dark-Sky Association. Dark Sky Society works to support educational and legislative efforts to reduce light pollution. http://www.darkskysociety.org/index.cfm
Light pollution isn't just about seeing the night sky. Ever notice how fresh and good the air smells in the early morning? That's because chemicals in the atmosphere break down the pollutants that accomulate during the day. Sunlight inhibits the chemical reactions that break down pollutants and clean the air, but recent research suggests that artificial lights have the same effect. This means that the accomulated results of light pollution are increasing the levels of air pollution worldwide. The government regulates the amounts of air pollution and works to decrease known air pollutants, so why are there no laws to decrease light pollution, a known link to air pollution?
 NYC
NYC
Another effect of light pollution is the health risks of it. People who live in light polluted areas tend to suffer from sleep problems, which can result in vision problems, heart disease, obesity, ADHD, OCD, and even cancers. The brain produces chemicals, including melatonin which also helps us sleep, to suppress tumors and kill off cancerous cells, but excessive light will hamper the brain's abilities to produce that chemical, resulting in an increased risk of cancer. Washington Post article Dr. Stephen M. Pauley wrote a paper on the effects of light pollution on human health: Dr. Pauley's paper
The local habitats also suffer from light pollution. Increased LAN (light at night) hurts night-blooming plants, which feed nocturnal animals, are dying from LAN. The animals which feed off of the plants die frm starvation, and the animals who hunt those animals are dying. Light pollution is destroying ecology, air quality and human health. Imagine a world filled with ADHD cancer patients who can't sleep and lie awake breathing terrible-smelling air and looking at skyglow listening to the silence because all the nighttime animals are dead. Lovely.
Let's celebrate Global Astronomy Month by working to preserve our night skies so that 100% of Americans will live where the Milky Way is clearly visible, 100% of children born in 2012 will see the Milky Way, including those in developed countries, and no one will have to suffer from city skyglow.
 Night sky in Antarctica
Night sky in Antarctica  Early evening sky in the Badlands, SD... This picture was taken shortly after sunset, before most of the stars are even visible.
Early evening sky in the Badlands, SD... This picture was taken shortly after sunset, before most of the stars are even visible.
60% of Americans live where the Milky Way is no longer even faintly visible?
50% of children worldwide will never see the Milky Way ever?
Of those 50%, 48% live in either the U.S, Canada, Europe or Asia?
1.5% live in the Middle East?
0.5% live in suburnized areas of Africa and South America?
The skyglow caused by London streetlights blocks stars and can be seen 125 miles away in French rural towns?
Worldwide, light pollution rises approximately 6% every year. It's estimated that by the end of the decade all Americans will live where the Milky Way is no longer visible, 90% of children will never see the Milky Way, and 50% of children will never see any stars, only the moon. Pretty scary statistics for amateur backyard astronomers.
April is Global Astronomy Month, so what better time to celebrate the night skies and educate about the effects of light pollution than now? The International Dark-Sky Associaton is fighting governments to pass laws to reduce the skyward-fixed lights and use lights that don't send off long-range light waves. The IDA has successfully caused over 300 cities to switch to better lighting that does not block out the night sky. Click here to learn more about the International Dark-Sky Association.
Globe at Night is another group dedicated to preserving our night skies. Every month, people world wide make observations of the night sky and send their results to Globe at Night. Globe at Night records the data and uses it to track the spread and growth of light pollution. The last opportunity to participate in Globe at Night for the next few months will be April 11-20. Click here to find out how.
In addition to participating in Globe at Night, I am a member of the Dark Sky Society, which is seperate from the International Dark-Sky Association. Dark Sky Society works to support educational and legislative efforts to reduce light pollution. http://www.darkskysociety.org/index.cfm
Light pollution isn't just about seeing the night sky. Ever notice how fresh and good the air smells in the early morning? That's because chemicals in the atmosphere break down the pollutants that accomulate during the day. Sunlight inhibits the chemical reactions that break down pollutants and clean the air, but recent research suggests that artificial lights have the same effect. This means that the accomulated results of light pollution are increasing the levels of air pollution worldwide. The government regulates the amounts of air pollution and works to decrease known air pollutants, so why are there no laws to decrease light pollution, a known link to air pollution?
Another effect of light pollution is the health risks of it. People who live in light polluted areas tend to suffer from sleep problems, which can result in vision problems, heart disease, obesity, ADHD, OCD, and even cancers. The brain produces chemicals, including melatonin which also helps us sleep, to suppress tumors and kill off cancerous cells, but excessive light will hamper the brain's abilities to produce that chemical, resulting in an increased risk of cancer. Washington Post article Dr. Stephen M. Pauley wrote a paper on the effects of light pollution on human health: Dr. Pauley's paper
The local habitats also suffer from light pollution. Increased LAN (light at night) hurts night-blooming plants, which feed nocturnal animals, are dying from LAN. The animals which feed off of the plants die frm starvation, and the animals who hunt those animals are dying. Light pollution is destroying ecology, air quality and human health. Imagine a world filled with ADHD cancer patients who can't sleep and lie awake breathing terrible-smelling air and looking at skyglow listening to the silence because all the nighttime animals are dead. Lovely.
Let's celebrate Global Astronomy Month by working to preserve our night skies so that 100% of Americans will live where the Milky Way is clearly visible, 100% of children born in 2012 will see the Milky Way, including those in developed countries, and no one will have to suffer from city skyglow.
Sunday, February 12, 2012
Our Weird Solar System
What would you say if I told you that the solar system is different from the space outside? Likely you'd look at me with a blank stare and say something along the lines of "and I care why?" Don't. It gets annoying. But seriously, the space outside of the solar system is different from the space inside, according to NASA's IBEX spacecraft. IBEX orbits Earth while scanning the skys for neutral atoms that can slip through the magnetic defences of the Heliosphere, the protective barrier formed by the sun's magnetosphere which protects the solar system from harmful outside radiaton.
What's so specifically different about the galaxy outside? The oxygen to neon ratio. Outside the solar system, there are approximately 74 oxygen atoms for every 20 neon atoms. Inside the solar system, there are approximately 111 oxygen atoms for every 20 neon atoms; a significant difference.
“There are at least two possibilities," says David McComas the principal investigator for IBEX at the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas. "Either the solar system evolved in a separate, more oxygen-rich part of the galaxy than where we currently reside or a great deal of critical, life-giving oxygen lies trapped in interstellar dust grains or ices, unable to move freely throughout space—and thus undetectable by IBEX."
While IBEX samples alien atoms from Earth orbit, NASA’s Voyager spacecraft have been traveling to the edge of the heliosphere for nearly 40 years—and they could soon find themselves on the outside looking in. Researchers expect Voyager 1 to exit the solar system within the next few years. The new data from IBEX suggest the Voyagers are heading for a new frontier, indeed.
For more information, check out the NASA article: http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2012/10feb_alienmatter/
What's so specifically different about the galaxy outside? The oxygen to neon ratio. Outside the solar system, there are approximately 74 oxygen atoms for every 20 neon atoms. Inside the solar system, there are approximately 111 oxygen atoms for every 20 neon atoms; a significant difference.
“There are at least two possibilities," says David McComas the principal investigator for IBEX at the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas. "Either the solar system evolved in a separate, more oxygen-rich part of the galaxy than where we currently reside or a great deal of critical, life-giving oxygen lies trapped in interstellar dust grains or ices, unable to move freely throughout space—and thus undetectable by IBEX."
While IBEX samples alien atoms from Earth orbit, NASA’s Voyager spacecraft have been traveling to the edge of the heliosphere for nearly 40 years—and they could soon find themselves on the outside looking in. Researchers expect Voyager 1 to exit the solar system within the next few years. The new data from IBEX suggest the Voyagers are heading for a new frontier, indeed.
For more information, check out the NASA article: http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2012/10feb_alienmatter/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)